- URL:https://<geoanalytics-url>/CalculateDensity
- Version Introduced:10.5
Description
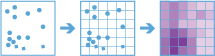
The CalculateDensity operation creates a density map from point features by spreading known quantities of a phenomenon (represented as attributes of the points) across the map. The result is a layer of areas classified from least dense to most dense.
For point input, each point represents the location of an event or incident, and the result layer represents a count of the incident per unit area. A higher density value in a new location means that there are more points near that location. In many cases, the result layer can be interpreted as a risk surface for future events. For example, if the input points represent locations of lightning strikes, the result layer can be interpreted as a risk surface for future lightning strikes.
Other use cases for this tool include the following:
- Create crime density maps to help police departments properly allocate resources to high crime areas.
- Calculate densities of hospitals within a country. The result layer will show areas with high and low accessibility to hospitals. This information can be used to determine where new hospitals should be built.
- Identify areas that are at high risk of forest fires based on historical locations of forest fires.
- Locate communities that are far from major highways to plan where new roads should be constructed.
Request parameters
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| inputLayer (Required) | The point layer on which the density will be calculated. Syntax: As described in Feature input, this parameter can be one of the following:
REST Examples |
| fields (Optional) | Provides one or more fields specifying the number of incidents at each location. You can calculate the density for multiple fields, and the count of points will always have the density calculated. REST Examples |
| weight (Required) | The type of weighting applied to density calculations. This parameter supports two values: Uniform (default), which calculates a magnitude-per-area, and Kernel, which applies a kernel function to fit a smooth tapered surface to each point. Values: Uniform | Kernel REST Examples |
| binType (Required) | The type of bin used to calculate density. Analysis using Square or Hexagon bins requires a projected coordinate system. When aggregating layers into bins, the input layer or processing extent (processSR) must have a projected coordinate system. At 10.5.1, 10.6, and 10.6.1, if a projected coordinate system is not specified when running analysis, the World Cylindrical Equal Area (WKID 54034) projection will be used. At 10.7 or later, if a projected coordinate system is not specified when running analysis, a projection will be picked based on the extent of the data. Values: Hexagon | Square REST Examples |
| binSize (Required) | The distance for the bins that the inputLayer will be analyzed using. When generating bins for the Square bin type, the number and units specified determine the height and length of the square. For the Hexagon bin type, the number and units specified determine the distance between parallel sides. REST Examples |
| binSizeUnit (Required) | The distance unit for the bins for which the density will be calculated and the linear unit to be used with the value specified for binSize. The default is Meters. Values: Meters | Kilometers | Feet | FeetInt | FeetUS | Miles | MilesInt | MilesUS | NauticalMiles | NauticalMilesInt | NauticalMilesUS | Yards | YardsInt | YardsUS REST Examples |
| timeStepInterval (Optional) | A numeric value that specifies duration of the time step interval. The default is none. This option is only available if the input points are time enabled and represent an instant in time. REST Example |
| timeStepIntervalUnit (Optional) | A string that specifies units of the time step interval. The default is none. This option is only available if the input points are time enabled and represent an instant in time. Values: Milliseconds | Seconds | Minutes | Hours | Days | Weeks| Months | Years REST Example |
| timeStepRepeatInterval (Optional) | A numeric value that specifies how often the time step repeat occurs. The default is none. This option is only available if the input points are time enabled and of time type instant. REST Examples |
| timeStepRepeatIntervalUnit (Optional) | A string that specifies units of the time step interval. The default is none. This option is only available if the input points are time enabled and represent an instant in time. REST Examples |
| timeStepReference (Optional) | A date that specifies the reference time to align the time slices to, represented in milliseconds from epoch. The default is January 1, 1970, at 12:00 a.m. (epoch time stamp 0). This option is only available if the input points are time enabled and of time type instant. REST Examples |
| radius (Required) | The size of the neighborhood within which density will be calculated. The radius size must be larger than the binSize value. REST Examples |
| radiusUnit (Required) | The distance unit for the radius defining the neighborhood for which density will be calculated and the linear unit to be used with the value specified for binSize. The default is Meters. Values: Meters | Kilometers | Feet | FeetInt | FeetUS | Miles | MilesInt | MilesUS | NauticalMiles | NauticalMilesInt | NauticalMilesUS | Yards | YardsInt | YardsUS REST Examples |
| areaUnits (Optional) | The output units of the density values. The default value is SquareKilometers. If density values are very small, you can increase the size of the area units (for example, square meters to square kilometers) to return larger values. This value only scales the result. Values: SquareMeters | SquareKilometers | Hectares | SquareFeet | SquareFeetInt | SquareFeetUS | SquareYards | SquareYardsInt | SquareYardsUS | SquareMiles | SquareMilesInt | SquareMilesUS | Acres | AcresInt | AcresUS REST Examples |
| outputName (Required) | The task will create a feature service of the results. You define the name of the service. REST Examples |
| context (Optional) | The context parameter contains additional settings that affect task execution. For this task, there are four settings:
|
| f | The response format. The default response format is html. Values: html | json |
Example usage
The example below is a sample request URL for CalculateDensity:
https://webadaptor.domain.com/server/rest/services/System/GeoAnalyticsTools/GPServer/CalculateDensity/submitJob?inputLayer={"url":"https://webadaptor.domain.com/server/rest/services/Hurricane/hurricaneTrack/0"&bintype=Hexagon&binSize=108.3&binSizeUnit=Meters&fields="classed_magnitude"&weight=Uniform&timeStepInterval=20&timeStepIntervalUnit=Minutes&timeStepRepeatInterval=1&timeStepRepeatIntervalUnit=Days&timeStepReference=946684800000&radius=10&radiusUnit=NauticalMiles&areaUnits=SquareMiles&outputName=myOutput&context={"extent":{"xmin":-122.68,"ymin":45.53,"xmax":-122.45,"ymax":45.6,"spatialReference":{"wkid":4326}}}&f=jsonResponse
When you submit a request, the service assigns a unique job ID for the transaction.
{
"jobId": "<unique job identifier>",
"jobStatus": "<job status>"
}After the initial request is submitted, you can use jobId to periodically check the status of the job and messages as described in Check job status. Once the job has successfully completed, use jobId to retrieve the results. To track the status, you can make a request of the following form:
https://<analysis url>/CalculateDensity/jobs/<jobId>
Access results
When the status of the job request is esriJobSucceeded, you can access the results of the analysis by making a request of the following form:
https://<analysis-url>/CalculateDensity/jobs/<jobId>/results/output?token=<your token>&f=json| Response | Description |
|---|---|
| output |
The output value will always contain polygon features. The number of resulting polygons is based on the location of the inputLayer value. The layer will have an attribute for each field on which the density has been calculated, as well as the density of the count of points.
The result has properties for parameter name, data type, and value. The contents of value depend on the outputName parameter provided in the initial request. The value contains the URL of the feature service layer. See Feature output for more information about how the result layer is accessed. |