Note:
This functionality is currently only supported in Map Viewer Classic (formerly known as Map Viewer). It will be available in a future release of the new Map Viewer.
 The Join Features tool transfers attributes from one layer or table to another based on spatial, temporal, and attribute relationships, or some combination of the three. Optionally, statistics can be calculated for the joined features.
The Join Features tool transfers attributes from one layer or table to another based on spatial, temporal, and attribute relationships, or some combination of the three. Optionally, statistics can be calculated for the joined features.
Workflow diagram
Analysis using GeoAnalytics Tools
Analysis using GeoAnalytics Tools is run using distributed processing across multiple ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server machines and cores. GeoAnalytics Tools and standard feature analysis tools in ArcGIS Enterprise have different parameters and capabilities. To learn more about these differences, see Feature analysis tool differences.
Examples
An analyst has crime data from throughout their city. To analyze and study the impact of these crimes, the analyst needs to understand the relationship that the crime locations have with the various city jurisdictions, such as school districts, police beats, and neighborhoods. By using the Join Features tool, additional information about each location can be appended to each crime, and the impact on various jurisdictions can be further studied and analyzed.
Tip:
If your portal is configured to use ArcGIS Living Atlas content, you can use the state and county ArcGIS Living Atlas layers, which include population data that can be joined to your crime data.
Usage notes
The Join Features tool is designed to transfer and append information from one layer to another. The information that is transferred is based on the type of spatial relationship defined, the temporal relationship defined, a common attribute that is shared between the two datasets, or some combination of the three.
When joining features, you can join features based on a spatial relationship, a temporal relationship, an attribute relationship, or a combination of the three.
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| The spatial relationship that will determine if features are joined to each other. The available relationships depend on the geometry type (point, line, or area) of the layers being joined. Available spatial relationships are as follows:
|
| The temporal relationship that will determine if features are joined to each other. The available relationships depend on the time type (instant or interval) of the layers being joined. Available temporal relationships are as follows:
|
| The attribute relationship that will determine if features are joined to each other. Features are matched when the field values in the join layer are equal to field values in the target layer. |
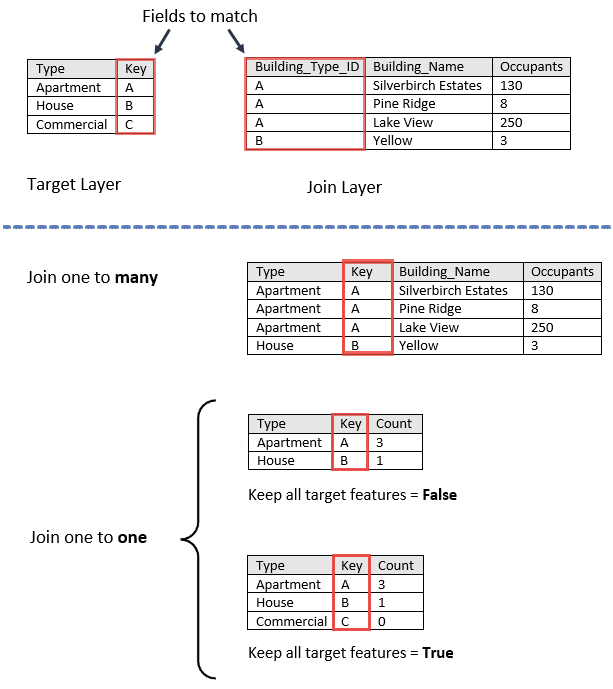
If multiple features match with the same target feature, you can determine if all the matching features will be joined (Join one to many) or if all the matching features will be summarized together (Join one to one) as follows:
- Join one to one—This option summarizes all of the matching join features to each feature in the target layer. Only the features that have a match will be included in the summary and output. The count of joined features will be added, in addition to other statistics such as sum, minimum, maximum, range, mean, variance, and standard deviation.
- Join one to many—This option joins all the matching features in the join layer to the target layer. The result layer will contain multiple records of the target feature.
You can optionally build an expression by which to join features. If you specify an expression, only features that meet the condition will be used. For example, you could only join target features from the field Magnitude if greater than the join feature with a field named Explosion, using the expression $target["Magnitude"] > $join["Explosion"]. Learn more about Arcade expressions with Join Features.
If Use current map extent is checked, only the features visible within the current map extent will be analyzed. If unchecked, all features in both the target layer and the join layer will be analyzed, even if they are outside of the current map extent.
Limitations
Summary statistics will only be calculated if a Join one to one operation is specified.
How Join Features works
The following describes how the Join Features tool works:
Calculations
Statistics are calculated for only those features that meet the specified spatial, temporal, or attribute relationship used in the Join one to one operation. You can calculate numeric and string statistics. By default, all statistics are calculated. Using the image above, numeric statistics were calculated on the Occupants field and string statistics were calculated on the Building_Name field for the values of Apartments for the Type field as shown in the following tables:
| Numeric Statistic | Results of Occupants of Type Apartment |
|---|---|
Count | Count of: |
Sum | |
Minimum | Minimum of: |
Maximum | Maximum of: |
Average | |
Variance | |
Standard Deviation | |
| String Statistic | Results of Occupants of Type Apartment |
|---|---|
Count | ["Silverbirch Estates", "Pine Ridge", "Lake View"] = 3 |
Any | = "Pine Ridge" |
Note:
The count statistic (for strings and numeric fields) counts the number of nonnull values. The count of [0, 1, 10, 5, null, 6] = 5. The count of [Primary, Primary, Secondary, null] = 3.
ArcGIS API for Python example
The Join Features tool is available through ArcGIS API for Python.
This example finds power outages in your state that may have been caused by a lightning strike. The tool will return all power outages that occur within 30 minutes after a lightning strike and within 20 miles of the strike.
# Import the required ArcGIS API for Python modules
import arcgis
from arcgis.gis import GIS
from arcgis.geoanalytics import summarize_data
# Connect to your ArcGIS Enterprise portal and confirm that GeoAnalytics is supported
portal = GIS("https://myportal.domain.com/portal", "gis_publisher", "my_password")
if not portal.geoanalytics.is_supported():
print("Quitting, GeoAnalytics is not supported")
exit(1)
# Find the big data file share dataset you'll use for analysis
search_result = portal.content.search("", "Big Data File Share")
# Look through the search results for a big data file share with the matching name
bdfs_search = next(x for x in search_result if x.title == "bigDataFileShares_NaturalDisaters")
# Look through the big data file share for lightning
lightning = next(x for x in bdfs_search.layers if x.properties.name == "Lightning")
# Find a feature layer named "PowerOutages" in your ArcGIS Enterprise portal
outages_search_result = portal.content.search("PowerOutages", "Feature Layer")
outages_layer = outages_search_result[0].layers[0]
# Set the tool environment settings
arcgis.env.verbose = True
arcgis.env.defaultAggregations = True
# Run the Join Features tool
output = summarize_data.join_features(target_layer = outages_layer,
join_layer = lightning,
join_operation = "JoinOneToMany",
spatial_relationship = "Near",
spatial_near_distance = 20,
spatial_near_distance_unit = "Miles",
temporal_relationship = "NearAfter",
temporal_near_distance = 30,
temporal_near_distance_unit = "Minutes",
output_name = "LightningOutages")
# Visualize the tool results if you are running Python in a Jupyter Notebook
processed_map = portal.map('yourState', 10)
processed_map.add_layer(output)
processed_map
Similar tools
Use the Join Features tool to transfer attributes from one layer or table to another based on spatial and attribute relationships.
Map Viewer Classic analysis tools
Use the Aggregate Points tool to aggregate points into areas.
ArcGIS Pro analysis tools
The Join Features tool performs the functions of the Spatial Join, Add Join, and Summary Statistics tools.
You can run the Join Features tool in ArcGIS Pro.


